Table of Contents
- Types of student visas in the USA
- Requirements for a student visa in the USA
- Required documents for a student visa in the USA
- Step-by-step visa application process
- When to apply for your student visa
- Post-study work visa in the USA
- Dependent visa
- Final thoughts
- Frequently asked questions
- Are visa interviews required?
- Can you work part-time with a student visa?
- Can you get a PR after a student visa?
- What if a student visa expires before the completion of studies?
- What happens if my visa application is rejected?
- How long is a student visa valid in the USA?
- How many years is an f1 visa valid for?
The USA is an attractive study-abroad destination for international students due to the invaluable academic opportunities. Many universities in the USA are highly ranked globally and offer internationally recognised degrees with excellent career advancement potential. In addition, the multicultural and welcoming environment of the country also makes it a preferred choice for international students.
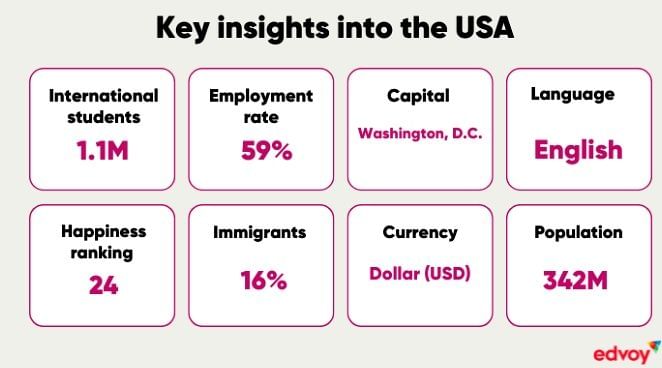
Moving to a new country is a big change in many ways: geographically, culturally, and psychologically. So, if you're concerned about the student visa in the USA, it’s likely that you'll have concerns about various other aspects of life in the USA. No worries. Our experts have sorted it out for you in the table below. Click on the topics you’re interested in and get the must-needed information you’re looking for.
| Student life in the USA | Best universities in the USA |
| Best courses in USA | Employment opportunities in the USA |
| Cost of living in the USA | Education system in the USA |
Getting a student visa is a lengthy (but required) process and involves significant documentation. However, with the right preparation and guidance, you can secure a student visa for the USA without much hassle. In this article, we’ve provided all the information you need to secure a student visa for your higher education in the USA. Keep reading to understand the details.
Types of student visas in the USA
There are three types of student visas available in the USA: F1, J1, and M1. These visas are issued for different types of academic programmes and also differ in their eligibility criteria. Here are more details about the three types of student visas.
| Type of visa | Description |
| F1 visa | An F1 visa is issued for pursuing full-time academic studies at accredited colleges, universities, and other institutions. It allows part-time on-campus work and Optional Practical Training for up to one year after course completion. You can also take up on-campus, part-time employment. |
| J1 visa | A J1 visa is issued to students who require practical training unavailable in their home country, but is essential to complete their academic programme. Employment similar to F1 is allowed with sponsor permission. |
| M1 visa | An M1 visa is issued to students attending non-academic or vocational schools. You cannot take up employment during your course. You must also prove sufficient funds for all tuition and living expenses during the stay. |
Requirements for a student visa in the USA
There are certain requirements you should meet to be eligible to apply for a student visa in the USA. From the documents to submit to the interview process, there are several criteria involved to ensure that you are a genuine student with the capability to support yourself during your studies.
Also read: Which countries are easiest to get PR after studies?
Required documents for a student visa in the USA
Take a look at the documents required to apply for a student visa in the USA.
- Passport: A passport that is valid for at least 6 months beyond your intended stay in the USA.
- SEVP acceptance: An acceptance at an SEVP-approved school.
- Form I-20 or DS-2019: This is provided by the institution that you are planning to attend in the USA.
- Application fee payment receipt: Proof that you have paid the application fee for the visa.
- D-160 confirmation page: Confirmation of having submitted the online non-immigrant visa application form.
- SEVIS fee receipt: You must pay the fee after receiving Form I-20.
- Admission letter: Official acceptance letter from the institution where you have applied.
- Academic records: Your transcript, degrees, and other certificates from previous educational institutions.
- Financial documents: Proof of your capability to pay the tuition fee and bear the living expenses. This includes bank statements, scholarship letters, or loan approval letters.
- Standardised test scores: These include English language proficiency scores and other tests such as GMAT, GRE, and SAT.
- Photograph: Your recent photograph that meets the visa photo specifications.
Language tests accepted in the USA
There is no specific English language test score required for the student visa in the USA. However, you must prove your English language eligibility to the university or college you are applying to.
Take a look at the accepted English language tests in various educational institutions in the USA and the required scores.
| Test | Required scores (Undergraduate) | Required scores (Postgraduate) |
| IELTS Academic | Overall 6.0 - 6.5 band | Usually 6.5 - 7.0 overall |
| TOEFL iBT | Generally, 80-90 overall | Typically 80+ overall |
| PTE (Pearson Test of English) | Around 50-57 | Usually 60-68 or above |
| Duolingo English Test | Scores accepted by some universities, often 90+ | Typically 105+ |
Financial requirements for a student visa in the USA
For a student visa in the USA, you must prove that you have sufficient funds to meet tuition and other living expenses at least for the first year of the programme. However, there is no fixed minimum amount specified by the authorities.
Take a look at the financial documents you have to produce as proof of your financial capability.
- Bank statements: Your recent bank statements for the last 3 to 9 months, which show sufficient funds to cover your study-abroad expenses.
- Proof of scholarships or grants: You can produce the official scholarship or grant award letter.
- Loan approval documents: Formal letters from banks or other financial institutions that confirm the loan amount and its approval.
- Sponsor's financial documents: The financial documents of your sponsor, which include bank statements and tax returns.
- Certificates of deposits or fixed deposits: Proof of any fixed deposits or other investments that you are using as financial security.
Step-by-step visa application process
The student visa application process involves several steps that you must follow, which include completing the application to upload documents, and attending interviews. You should carefully complete the application form and also meet the legal requirements to improve your chances of securing the student visa. Here are the steps involved in the student visa application process.
Get the Form I-20
Once you receive the admission letter from the university, provide an affidavit of support and financial documents to the university. You’ll then receive the Form-12 from the university, which contains the information shared with the Student Exchange and Visitor Information System (SEVIS).
Pay the I-901 SEVIS fee
Create your account on the SEVIS portal and pay the fee. Save the confirmation of fee payment for your records, and also for the visa interview.
Submit the DS-160 application
Complete the DS-160 application and pay the MRV fee. You must submit your passport, photo, and Form I-20 along with the application.
Schedule the visa interview
Check with the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate and schedule the visa interview. Since the wait time can be long, it’s recommended to schedule the interview as early as possible.
Attend the interview
Prepare the documents and attend the interview. The documents include your passport, Form I-20, DS-160 confirmation page, I-901 SEVIS fee payment confirmation, photograph, and MRV fee payment receipt.
When to apply for your student visa
The student visa application and processing may take time and could also involve processing delays. So it is advised to apply early for the student visa. Apply as soon as you receive the Form I-20. You can apply up to 365 days before the start date of your academic programme. The entire process of applying for the visa to uploading the documents, and attending interviews may take several weeks to months. There can also be delays due to the embassy workload.
Post-study work visa in the USA
A post-study work visa allows you to extend your stay and take up employment after completing the course. The most common work visa is the Optional Practical Training, which allows you to work for up to 12 months. STEM graduates can extend this for up to 24 months.
You can apply for the post-study work visa by submitting the Form I-765 to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), with guidance from their Designated School Official (DSO). This visa helps you gain practical experience and transition into longer-term work visas like the H-1B.
Dependent visa
You can use the dependent visa to bring immediate family members with you during your studies. Family members include your spouse and unmarried children under 21 years. The common dependent visas are F-2, H-4, J-2, and L-2. You can use your marriage certificate or birth certificate as proof of relationship.
Dependents can apply for their visa through the U.S. consulate or embassy by submitting their visa applications and attending interviews. However, dependents must have a separate Form I-20 to schedule the interview.
Final thoughts
International students planning to pursue their higher education in the USA must obtain a student visa. The student visa allows you to stay and study the desired course in educational institutions in the USA. Applying for a student visa may be a complex process. However, a good understanding of the process, documentation, and interview will help you apply successfully and secure the student visa. If your immediate family members wish to accompany you, they can apply for a dependent visa, which allows them to stay in the USA and support you.
If you're seriously considering the USA for your higher studies, we have a good number of partner universities where you can apply for your preferred courses.
We’re a global technology-driven admissions platform offering study-abroad solutions to students across the world. Our AI-powered app simplifies course search, the application process, and enrollment in international universities. With 18+ years of experience, we’ve helped 100K+ students from over 65 countries to pursue their study-abroad dreams. You could be the next!
Let our counsellors clear all your concerns and help you start your study-abroad journey right away!
Frequently asked questions
Are visa interviews required?
Yes, visa interviews are required as part of the student visa application process. During the interview, your eligibility, financial resources, and student intent will be assessed. There may be exceptions which you can check with the embassy or consulate.
Can you work part-time with a student visa?
Yes, if you hold an F-1 visa, you can work part-time for up to 20 hours per week on campus. During official breaks and annual holidays, you can work full-time. Off-campus work is also allowed, subject to authorisation through Optional Practical Training (OPT) or Curricular Practical Training (CPT).
Can you get a PR after a student visa?
Yes, it's possible to secure permanent residency after a student visa. It’s not a direct transition. You must meet the specified eligibility criteria, such as employer sponsorship.
What if a student visa expires before the completion of studies?
If your student visa expires before the completion of your studies, you must act immediately and contact your university's international office for guidance. You can apply for a visa extension or a new visa by submitting the necessary documents, such as a passport and financial proof.
What happens if my visa application is rejected?
If you do not fulfill the student visa criteria for the United States and your visa application is refused, the decision is final, and you will not be able to appeal. The good news is that you may reapply and request a waiver of ineligibility.
How long is a student visa valid in the USA?
F1 students can stay in the US for up to 60 days after finishing their academic programme unless they have applied for and been granted to stay and work for a time period under the OPT Program. M1 - This is a non-immigrant permit with a one-year validity period. However, students may ask for an extension of up to three years. M1 Visa holders can only study part-time under certain conditions and for a maximum of six months.
How many years is an f1 visa valid for?
F-1 student visas are typically valid for five years from the beginning of your study.