Get a complete guide to studying in Canada.
Canada is a popular destination for international students due to its high-quality education, global exposure, excellent employability, and multicultural environment. There are several prestigious universities offering internationally recognised degrees and a safe environment. The flexible employment policies, including post-study work opportunities, make Canada an ideal choice for international students.
Here are some key insights into the advantages of Canada:
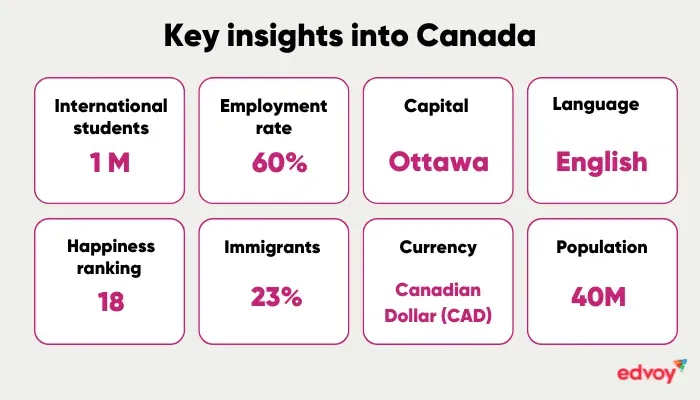
Get a complete guide to studying in Canada.
Moving to a new country is a big change in many ways: geographically, culturally, and psychologically. So, if you're concerned about the education system in Canada, it’s likely that you'll also have concerns about various other aspects of life. No worries. Our experts have sorted it out for you in the table below. Click on the topics you’re interested in and get the information you’re looking for.
| Student life in Canada | Student visa in Canada |
| Education system in Canada | Cost of living in Canada |
| Best universities in Canada | Best courses in Canada |
The education system in Canada is a blend of academic and real-world learning, preparing you to meet the challenges of the industry. If you wish to explore more about Canada’s education system, keep reading!
Overview
The education system in Canada has three levels: elementary, secondary, and post-secondary education. Primary and secondary education lasts for 12 years, and the curriculum is defined by the provincial government. On completing Grade 12, you’ll receive a high school diploma and become eligible to enter post-secondary education. Post-secondary education covers colleges, universities, and vocational schools.
Education in Canada is regulated by provincial and territorial governments. Each province has its own Ministry of Education for setting academic standards, curriculum development, and funding allocation. The post-secondary education is supported by the federal government through funding and supports access for minority communities.
Highlights
A country’s education system plays a crucial role in deciding the quality of education offered by its institutions. A well-structured system ensures to maximise your overall development and equips you with a solid academic foundation and practical knowledge.
Canada’s education system offers a wide range of career-focused programmes to international students, ranging from arts and technology to vocational training. It provides a rigorous learning environment where you can grow to your full potential.
Take a look at the highlights of Canada’s education system.
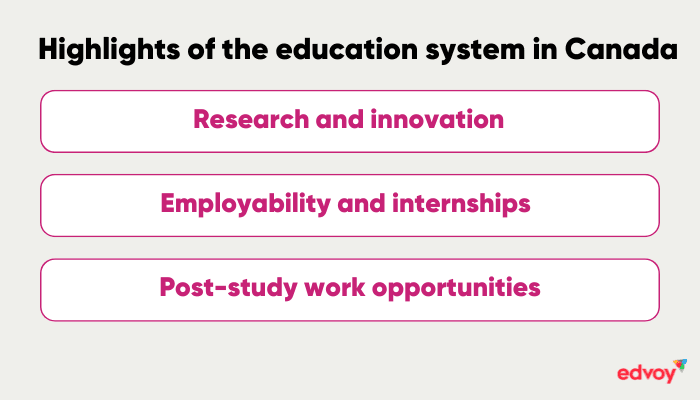
Research and innovation
Canada has world-class universities with a strong focus on research and innovation. Research-based learning develops your curiosity and critical thinking. The universities invest heavily in research facilities and encourage you to explore the latest in your industry.
Employability and internships
Canadian universities maximise your employability through practical exposure and internship opportunities. With their strong industry connections, the universities provide various events and workshops supporting you in expanding your network and gaining industry insights.
Post-study work opportunities
Canada’s Post-Graduation Work Permit allows you to stay for up to 3 years and gain valuable work experience, allowing you to work for most employers without requiring employer sponsorship.
The higher education landscape
Higher education has a key role in your personal and professional development, equipping you with relevant knowledge and critical thinking skills to meet the challenges of the international job market. With a focus on interdisciplinary learning and digital literacy, today’s higher education ensures that you are prepared to handle roles across multiple disciplines.
The universities in Canada are ranked highly globally and include renowned ones such as the University of Toronto and McGill University. You can access high-quality education and impactful research and explore a number of career-focused undergraduate degrees, master's and doctoral programmes.
Take a look at the section below for more information about the study levels in Canadian universities.
Study levels
Canada offers three main academic intakes: September (fall), January (winter), and May/June (summer). The most popular is the September intake, where you have the largest selection of courses.
Here are the study levels available across the three intakes.
| Study level | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Preparatory programmes for students who do not meet direct entry requirements for undergraduate courses | 1 year or less |
| Vocational | Certificate or diploma programmes focused on practical skills for direct employment or further education. | 6 months to 2 years |
| Undergraduate | Bachelor’s degree programmes that combine general education with specialisation. | 3-5 years |
| Postgraduate | Master’s degrees, graduate diplomas, and certificates emphasising advanced knowledge | 1 to 3 years |
| Doctoral | The highest level of academic degree, involving advanced coursework and original research leading to a thesis. | Typically 4-6 years |
Undergraduate courses
Canadian universities offer you a variety of undergraduate programmes that are designed to enhance your specialised knowledge and professional skills in your subject area. With a multidisciplinary approach, these programmes provide good internship opportunities and maximise your employability.
Here are more details about the types of undergraduate courses in Canada.
| Types of undergraduate courses | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bachelor of Arts (BA) | 3-4 years | Focuses on humanities, social sciences, and arts |
| Bachelor of Science (BSc) | 3-5 years | Focuses on natural sciences, technology, and mathematics |
| Bachelor of Commerce (BCom) | 3-4 years | Focuses on business, accounting, finance, and management principles |
| Specialised degrees | 4-5 years | Includes programmes like engineering, computer science, and other technical fields. |
Postgraduate courses
Postgraduate courses provide advanced qualifications that provide subject matter expertise and enhance your employability. These programmes also focus on improving your leadership skills, preparing you for the international job market.
Here are more details about the types of postgraduate courses in Canada.
| Types of postgraduate courses | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Postgraduate Certificate | 8 months - 1 year | Short programmes focusing on skill enhancement |
| Postgraduate Diploma | 1 - 2 years | Provides advanced practical knowledge and skills |
| Master’s Degree | 1 - 2 years | Focused on coursework and professional skills development |
| Doctoral (PhD) | 4 - 7 years | In-depth original research leading to a dissertation |
Get a complete guide to studying in Canada.
Cost of education
Since international education is expensive, it’s ideal that you gain an understanding of the possible costs you might incur during your academic life in Canada. This will help you plan your finances wisely and maintain your expenses within the budget. A major component of your expenses is the tuition fee.
Here's an insight into the annual tuition fees in Canada.

Your overall cost will also include accommodation, travel, healthcare, and other miscellaneous expenses. The annual accommodation cost in Canada ranges between CAD 6,000 and CAD 15,000, and food expenses between CAD 3,000 and CAD 4,800.
You can expect travel expenses between CAD 1,000 and CAD 2,000. In addition, keep a budget between CAD 1,000 and CAD 3,000 for miscellaneous expenses.
To help manage your educational costs, Edvoy Funds can be an excellent resource. Edvoy Funds connects you with 10+ financial institutions that provide pre-approved education loans in 72 hours.
Download our all-in-one Edvoy app and try the “Funds” feature.
Final thoughts
Canada is a popular study-abroad destination offering you high-quality education and excellent international career prospects. You can choose from a wide range of career-focused programmes, ranging from arts and technology to vocational training. The highly ranked universities provide a rigorous learning environment and ample practical exposure, preparing you to handle real-world challenges. With the availability of numerous courses spread across foundation, undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral levels, you can easily find the right course that suits your aptitudes and career goals.
If you're seriously considering Canada for your higher studies, we have a good number of partner universities where you can apply for your preferred courses.
We’re a global technology-driven admissions platform offering study-abroad solutions to students across the world. Our AI-powered app simplifies the course search, application process, and enrollment in international universities. With 18+ years of experience, we’ve helped 100K+ students from over 65 countries to pursue their study-abroad dreams. You could be the next!
Let our counsellors clear all your concerns and help you start your study-abroad journey right away!
Frequently asked questions
How many years are there in secondary school in Canada?
The number of years to complete secondary school in Canada varies across the provinces. However, on average, it takes 12 years to complete secondary school.
How old are juniors in high schools in Canada?
Juniors in Canadian high schools are usually 16 or 17 years old. The age will vary based on when a student starts school and the curriculum of the province.
What does high school mean in Canada?
The term high school in Canada refers to the final stage of education and covers grades 9 to 12. The students in high school are usually between 14 and 18 years of age. The curriculum includes compulsory subjects like math and science, and also electives.
When does school start in Canada?
School starts in Canada in late August or early September. The exact date may vary based on the province and school district. To know the exact start date, check the calendar of the school.
At what age do you go to university in Canada?
To go to a university in Canada, you should be 18 years of age. However, you can also start at age 17, if you have parental or guardian consent. You should also meet the admission and visa requirements.
How does Canada's school system work?
Canada follows a decentralised education system where each province and territory manages its K-12 public education. The structure is divided into primary and high schools, and each province sets its curriculum and education policies.