So you’ve got your eye on studying abroad in the USA? Your next step after getting accepted by a university is to get yourself a student visa for the USA.
If you’re still only considering heading to America for university by the way, check out our article on Reasons why you should study in the USA. Maybe that’ll convince you that it’s a good call!
One of the more complicated things about studying in the USA is the student visa process, but it’s worth the effort. Knowing which visa you need, what the requirements are, and how to apply is a little bit of a minefield if you go it alone. But here are Edvoy, we want to enable students like you, so we’ve done the research on US student visas so you don’t have to!
In this article, we take you through which US student visas there are, who they’re for, and what you have to do to get one.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- Which US student visa do I need?
- 1. F1 Student Visa
- 2. J1 Exchange Visitor Visa
- 3. M1 Student Visa
- 4. US student visa requirements & rules
- 5. How to get a student visa for the USA
Which US student visa do I need?
1. F1 Student Visa
The F1 visa is the most common student visa for international students in the US. This is for students who are planning on studying a full-time academic university course, and is administered to undergraduates and postgraduates alike.
If the above sounds like you, i.e. you’ve applied to study full time at a university in the USA, then you need an F1 visa. We’ve gone into some detail further down on the F1 visa requirements and documents you’ll need to apply.
Oh and by the way, If you want to bring children or a spouse along with you to the US, they must get an F2 Visa to go along with your F1 visa. This allows them to stay with you while you study in the USA, but it’s worth noting that the F2 visa does not allow them to work while in the US.
If you’re looking to study in the US, but not on a full time or academic course, check out these options below!
Also Read: How to avail your US Student visa?
2. J1 Exchange Visitor Visa
The J1 Exchange Visitor Visa is for students who are planning to study a vocational (i.e. non - academic) course with a duration of up to 10 months.
In the case of children, dependents or spouses who might want to stay with you while you study, they will have to apply for a J2 visa instead. Like the F2 visa mentioned above, this visa does not permit them to work -- though with prior permission established in your application, this can be subject to change.
Also Read: Types of Student Visas
3. M1 Student Visa
The M1 student visa is only applied for by people who want to study a vocational course, such as a technical trade like mechanical or culinary skills. The M1 visa only allows you to stay in the US for the duration of your course of study, after which you have to leave the country.
4. US student visa requirements & rules
Now that you know which visa you need, it’s useful to know what the requirements are for documentation to submit with your application.
By the way, if you’re still not sure which US student visa you need, just hit the chat button on the Edvoy homepage and let us help.
Below you can find a list of the things you’ll need for each visa application
F1 Student Visa requirements
- A passport that is valid for at least six months beyond your planned stay in the USA. If your passport is due to expire, you’ll have to apply for a new one.
- University I-20 form. This is a standard document that certifies that you’ve been accepted into a full time university course in the US.
- A print out of the visa application form you filled out online (DS-160). We’ll go into more detail on this below!
- Visa interview appointment letter. Once you complete the above-mentioned form, you’ll be directed to book an appointment at your nearest US consulate, after which you receive this letter.
- Original mark sheets, certificates and transcripts.
- Original English language assessment test certificate (GRE, GMAT, TOEFL, IELTS, Duolingo etc.) scorecard.
- Bank statements for the last 3 years, to prove that you have enough money to support your stay in the US. If a parent/guardian is supporting you through your education, you can give their bank statements also. If you think you’ll need financial support, check out our article How to apply for a scholarship to study abroad.
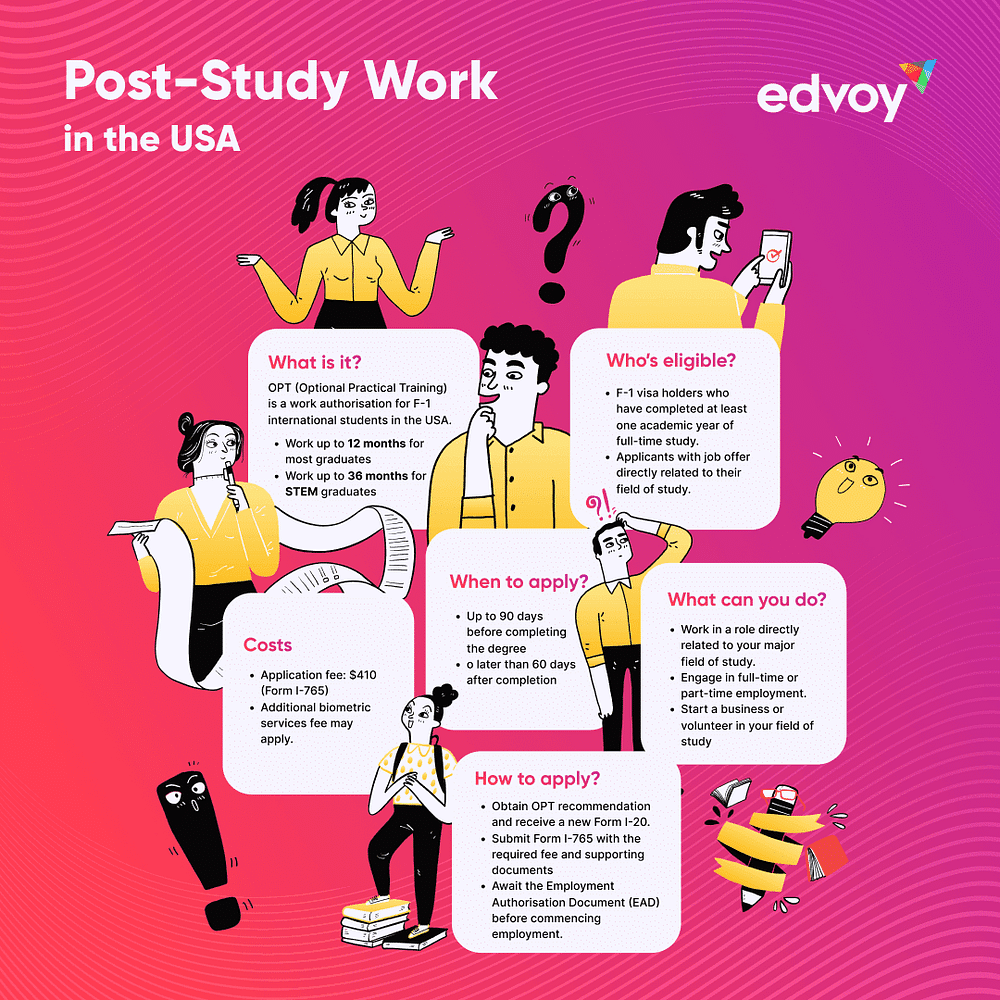
Want to work in the USA after graduation? This visual guide breaks down the OPT process, eligibility, and timelines for international students.
J1 Exchange Visitor Visa requirements
- DS-2019 Form, Certificate of Eligibility for Exchange Visitor Status
- DS-7002 Form, A Training/Internship Placement Plan (for exchange visitor trainees or intern visa applicants)
- Form DS-160, Online Nonimmigrant Visa Electronic Application
- A passport valid for travel to the U.S with validity six months after the intended period of stay in the US
- A passport-size photograph
Also read: Which countries are easiest to get PR after studies?
M1 Exchange Visitor Visa requirements
- A passport that is valid for at least six months beyond your planned stay in the USA. If your passport is due to expire, you’ll have to apply for a new one.
- Your DS-160 confirmation page
- Your visa appointment letter
- A passport-size photograph
- Receipts that prove you have paid your fees
- Your I-20 form (one original and one and one copy)
- Proof of your educational qualifications such as degrees and diplomas, transcripts, standardized test scores etc
- Bank statements for the last 3 years
Also Read: How to Prepare for US Student visa interview
5. How to get a student visa for the USA
So you know which visa to get (most likely the F1 visa) and what the requirements are. Now it’s time to apply!
Fortunately for you, we’ve already written a full walkthrough to help you get your student visa for the USA. Check out our article A step-by-step guide to applying for a US student visa!
Looking to study abroad? Let Edvoy make it easier for you! Check out our amazing partner universities in the world’s best study abroad countries! Click here to get started!
Found this helpful? Sign up and start planning your study-abroad journey today.